This page addresses some of the F (and N) class issues
which you may find in the the Dutch ham radio exam.
With thanks to Niek Hilbers of the Dutch VERON ham radio
club. It helped me to pass my exam with success.
Here is some of the home-work we were given (still N level):
1.
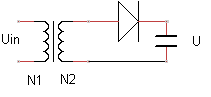 Uin
= 200 Veff
Uin
= 200 Veff
C = 4700 µF
N1 = 1000 wdgs
N2 = 100 wdgs
What is the value of U (onloaded)?
A. ± 2,800 V B. ± 2,000 V C. ± 20 V D. ± 28 V
2. What is the right formula for frequency:
A. f = T/1 B. f = 2ΠR C. f = 1/T
A. 0 V B. 1 V C. 2 V D. 3 V
A. High voltage amplification
B. Voltage amplification with value = 0
C. Low voltage amplification
A. mixing circuit
B. high frequency amplifier
C. oscillator
D. modulator
A.
B.
C.
D.
7.
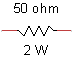 What
is the maximum allowable current?
What
is the maximum allowable current?
A. 25 mA
B. 40 mA
C. 200 mA
A. 0 Amp
B. 1 Amp
C. 2 Amp
D. 4 Amp
9.
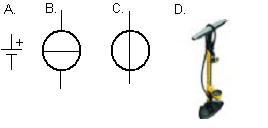 Which
symbol represents a current source:
Which
symbol represents a current source:
A, B, C or D
10.
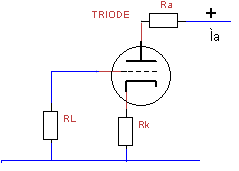 The
screen grid voltage -Ug is calculated with
the following formula:
The
screen grid voltage -Ug is calculated with
the following formula:
A. Ig * RL .
B. Ua / Ra .
C. Ua / (Ra+Rk) .
D. Ia * Rk .
11.
A 16 kHz analogue sound should be sampled using a sample
frequency of:
A. 34 kHz B. 25 kHz C. 16 kHz D. 8 kHz.
12.
Quantization noise is caused by:
A. rapid variation of signals B. square waves C. slow variation of signals.
13.
This number: 110011 represents:
A. binaire code B. analogue code C. hexadecimal code D. 6 tone code.
14.
Which mode of modulation is truly digital?
A. AM B. CW C. BPSK D. FSK
15. Ohm's law. Some elementary questions. Chapter 1. in the F book from the VERON.
a. The voltage is propotional to the current and the resistance.
b. The resistance is proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the current
c. The resistance is inversely proportional to the voltage and proportional to the current
d. The resistance is inversely proportional to the current and the voltage.
16.
a. 10 Amp.
b. 2 Amp.
c. 1.5 Amp.
d. 0 Amp.
17.
a. 8 Ω
b. 4 Ω
c. 2 Ω
d. 0.5 Ω
18.
a. Volt; b. watt; c. watt/sec.; d. Joule
19.
a. 0.004 Watt; b. 0.04 Watt, c. 0.4 Watt; d. 4 Watt
20.
a. ½ x
b. 2 x
c. 4 x
d. remains the same.
21.
U1 = 4 V.; U2 = 8 V. In resistor R is
4 Watt being dissipated.
When S is switched, how much Watt is than dissipated in R ?
a. 1 W
b. 2 W
c. 8 W
d. 16 W
22.
a. 10 V
b. 9 V
c. 1 V
d. 0 V
23.
What is the short-circuit current in the above picture ?
a. infinite b. 10 A c. 9 A d. 1 A
24.
a. 5 A
b. 3.5 A
c. 2 A
d. 1 A
25.
What is the unit of electric charge ?
a. Φ b. Ampère c. Coulomb d. Joule
26.
A battery of 40 Ah is being discharged in 10 hours. The average current was:
a. 400 A b. 40 A c. 4 A d. 0.4 A
27.
Why is a very high voltage being used when transporting electricity over long distances?
a. Then the current is small
b. the loss of energy is small
c. this is just the way it is being done
28.
How often does one need to use one's call sign during a QSO ?
a. at the beginning and at the end of a QSO
b. every time when the microphone (or key) is passed on to the other party
c. every five minutes
d. this is just for dumbo's
29.
a. 0 V.
b. 2 V.
c. 4 V.
d. 8 V.
30.
a. 0.5 A
b. 1 A
c. 1.5 A
d. 2 A
31.
a. very high
b. dependant of the current
c. low
d. zero
32.
The characters R F are spelled with the NATO alphabet as:
a. Radio - Fox ; b. Romeo - Fox ; c. Radio - Foxtrot ; d. Romeo - Foxtrot
33.
A radio-electrical transmission installation consists of:
a. A transmitter with its antenna ; b. the transmitter ; c. the transceiver ; d. the transceiver with its antenna.
34.
The unit for the magnetic field is:
a. V/m b. A/m c. V.m. d. Am
35.
The unit for the electro-magnetic field is:
a. V/m b. Watt/m c. Watt/m2 d. A.V/m
36.
a. 8 Volt
b. 5,6 Volt
c. 4 Volt
d. 2 Volt
37.
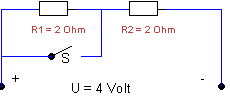 How
much power is used in this diagram with an open and a closed
switch?
How
much power is used in this diagram with an open and a closed
switch?
a. 4 and 2 watt
b. 4 and 4 watt
c. 4 and 16 watt
d. 4 and 8 watt
38.
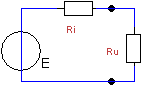 E
= 20 Volt; I = 1 A. URi = 2 Volt; URu
= 18 Volt. What is the value of Ri ?
E
= 20 Volt; I = 1 A. URi = 2 Volt; URu
= 18 Volt. What is the value of Ri ?
a. 0.5 Ω
b. 1 Ω
c. 2 Ω
d. 4 Ω
39.
a. 3 km/h b. 300,000 km/h c. 300,000 km/s d. 300,000,000 km/s
40.
a. the wave length b. the delay factor c. light d. the conductor
a. 0 Volt
b. 7 Volt
c. 5 Volt
d. 4 Volt
a. 6 Volt b. 4.5 Volt c. 3 Volt d. - 1.5 Volt
b. 100 Hz
c. 500 Hz
d. 1 kHz
44.
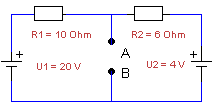 UAB
= ?
UAB
= ?
a. 15 Volt
b. 10 Volt
c. 6 Volt
d. 16 Volt
45.
The effective voltage of a sinus AC with an amplitude of
20 Volts is (approx.) ?
a. 6.4 Volt b. 7 Volt
c. 12.8 Volt d. 14 Volt
46.
Is a ham operator allowed to work with other CB operators
on 27 MHz ?
a. as compliant with the regulations: only with other
ham operators.
b. only if his transmission power stays within the power
limits
c. of course
d. only if approved equipment (CE) for CB usage is being
used.
47. A 100 Watt AM transmitter is approximately equal to:
a. 100 Watt FM transmitter with 5 kHz frequency sweep
b. 50 Watt SSB transmitter
c. 25 Watt SSB transmitter
d. 400 Watt SSB transmitter
a. 15 b. 12.5 c. 2 d. 0.5
49. The transmitter of question number 48 has a bandwidth of:
a. 15 kHz b. 7.5 kHz c. 5 kHz d. 2.5 kHz
50. Which modultion-type contains 100% information in the signal?
a. FSK b. AM c. CW d. PM
51.
Here
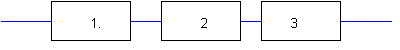 a
signal gets digitized. What is the right order?
a
signal gets digitized. What is the right order?
a. 1. sampler 2. D/A converter 3. reconstruction filter
b. 1. anti aliassing filter 2. sampler 3. A/D converter
c. 1. anti aliassing filter 2. sampler 4. D/A converter
d. 1. sampler 2. anti aliassing filter 3. A/D converter
52.
What is the characteristic of a binairy system ?
a. it has a number sequence from 1 to 10
b. it has 6 numbers and 6 characters
c. it is a logarithmic system
d. it represents two switching levels
a. an analogue method b. switching using BPSK c. switching using FSK d. switching using PSK on different levels
54.
A five bits PSK signal has:
a. 128 positions b. 64 positions c. 32 positions d. 16 positions
55.
The speed of a digital signal is given as:
a. kHz b. bits/second c. byte/second d. bit * second
R1 = 4Ω
R2 = 6Ω
UAB = ?
a. 0 Volt b. 2 Volt c. 4 Volt d. 18 Volt
57.
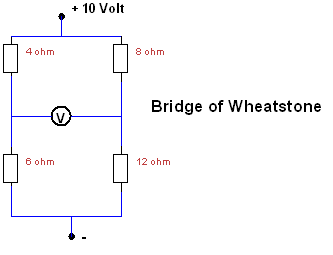 What
voltage does the Volt meter show?
What
voltage does the Volt meter show?
a. 10 Volt
b. 8 Volt
c. 2 Volt
d. 0 Volt
58.
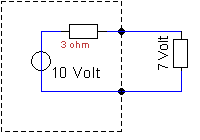 What
is the value of the short circuit current?
What
is the value of the short circuit current?
a. 0 A.
b. 1 A.
c. 3.33 A.
d. 7.4 A.
59.
With AMTOR ARQ:
a. there is no error correction b. each character is sent twice c. the other 'party' gives an acknowledgement d. is only used with FSK
60.
When a 100 Watt carrier is 100% AM modulated:
a. is the PEP 400 Watts b. is the PEP 100 Watt c. is the PEP 50 Watt d. is the PEP 25 Watt
61.
How do we call the broadband noise that has
an equal amplitude across the whole spectrum?
a. quantisising noise b. brown noise c. cosmic noise d. white noise.
62.
Why do we need to sample an analogue signal before we can
send it digitally?
a. to obtain the different voltage levels required by the A/D converter b. to allow the phase jumps in the HF signal c. to avoid quantisising noise d. with no sampling one gets aliassing.
63.
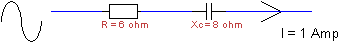 How
much power is dissipated in this configuration ?
How
much power is dissipated in this configuration ?
a. 6 Watt b. 8 Watt c. 10 Watt d. 14 Watt
64.
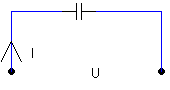 Which
statement is correct?
Which
statement is correct?
a. the current and voltage are in phase
b. the voltage is leading the current
c. the current is leading the voltage
d. the current lags the voltage
a. C = 1/2∏f.Xc b. C = 2∏fc c. C = 2∏F/Xc d. C = Xc/2∏f
a. 0 V. b. 2 V. c. 4 V. d. 6 V.
67.
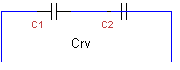 C1
= C2 = 10µF. What is the replacement value Crv
?
C1
= C2 = 10µF. What is the replacement value Crv
?
a. 20µF b. 10µF c. 5 µF d. 2.5 µF
68.
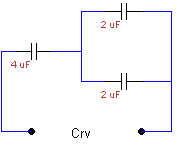 Crv
= ? (RV stands for replacement value)
Crv
= ? (RV stands for replacement value)
a. 2µF
b. 0.8 µF
c. 8µF
d. 5µF
78.
How large is the impedance of a coil using
VDC ?
a) equal to R b) √XL2 + R2 c) 1/√XL2 + R2 d) very high
79.
The formula for impedance XL is:
a) XL = 1/2∏f.L b) XL = 2∏f/L c) XL = 2∏f.L
d) XL = ω/2∏f.L
80.
Coils in HF circuits are shielded using:
a) aluminium b) wood c) tinplate d) magnetic tinplate
81.
The unit for the magnetic field H is:
a) Henry b) A/m c) Am d) V/m
91.
With a secundaire assignment of an amateurband the amateurs need to:
a. give priority to all other users
b. give priority to all other
secundary users
c. give priority to primary users
d. doesn't matter what
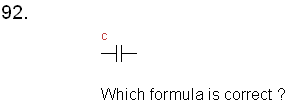 a.
Q = c.u
a.
Q = c.u
b. c = u/Q
c. c= Q/u2
d. c = Q/u
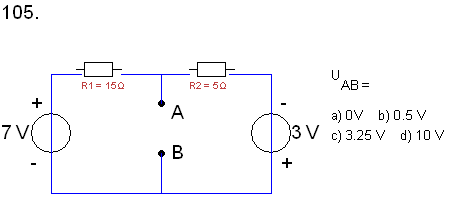
109. The collector dissipation of assignment 108 is:
a) 0 W b) 3 mW c) 10 mW d) 13 mW
111. The current in assignment 110. is 1 A. How much power is being dissipated?
a) 0 W b) 4 W c) 5000 W d) 5004 W.
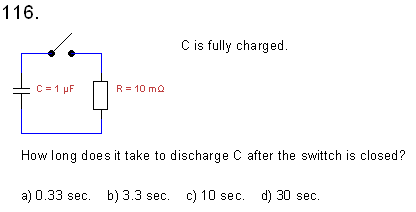
117.
Which statement is
correct?
a) at a capacitor
the current leads the voltage
b) at a capacitor the voltage leads the current
c) at a coil the current leads the voltage
d) none of the above is correct.
119.
A lead-acid battery of 12
Volt contains:
a) 1 cell b) 6 cells c) 10 cells d) 12 cells
122.
A practical value for a Pulse Width Modulator in a switching power supply is:
a) 10 Hz b) 50 Hz c) 1 kHz d) 15 kHz
125.
A radio amateur is asking a
fellow radio amateur to deliver a message to his
neighbour. This is:
a) allowed b) allowed unless it is a commercial message c) not allowed
126.
Home made equipment (receiver) is:
a) allowed b) not allowed c) allowed, provided it complies to certain specifications d) allowed, provided it is approved by the appropriate government agency
132. A PLL circuit uses what type of oscillator?
a) Collpits b) Hartley c) crystal d) VCO
Note: Voltage reduced i.e. less positive (+); Voltage increases i.e. more positive (+).
145.
A device is using 2700 joules during 15 minutes.
What is the power consumption of that device?
a) 3 W b) 180 W c) 675 W d) 2700 W
a) 0.5 b) 2 c) 12.5 d) 15
147.
In order to gain one (1) S-point, the transmit
power should:
a) not change b) increase four
(4) times c) increase two (2)
times
d) increase ten (10) times
a) The power amplifier (PA) of the transmitter
is set in class C.
b) The squelch of the receiver is set to tight
c) the transmitter has a sweep that is too large
d) the transmitter has a sweep that is too small
149.
The nearby selectivity of a receiver is
determined by:
a) the tuning at the input b)
the balance mixer
c) a high quality crystal filter in the MF
circuit d) a DSP audio unit.
150.
FM is being modulated with:
a) a diode detector b)
FM-discriminator c) a
product-detector
d) a flank-detector
a) putting a low pass filter in the modulator
b) putting a low pass filter in the antenna of
the transmitter
c) putting a high pass filter behind the
transmitter
d) to only work FM
a) install a pre-amplifier near the antenna
b) install a pre-amplifier near the receiver
c) apply a large MF amplification
d) apply a large LF amplification
153.
A noise having an equal
amplitude over a large bandwidth is called:
a) thermic noise b) cosmic noise c) white noise d) brown noise
Here I end my contribution to get familiar with the F license stuff, knowing there are many more items I could (or should) have addressed.